Introduction
Recently, I was exploring auditing functionality in Dynamics 365 CRM after 2022 Wave 1 release. I found that there are many enhancements that have happened in the recent release in the way you manage the audit in Dynamics 365 CRM.
With the expanded auditing capabilities of Dynamics 365 CRM, now you can manage the audit logs much more effectively.
Auditing can greatly increase your chances of staying on top of things but remember that this can significantly increase the size of the organization’s database. Occasionally you may want to stop auditing for maintenance purposes. When you stop auditing, the audit logs tracking will stop for an organization until you start it again.
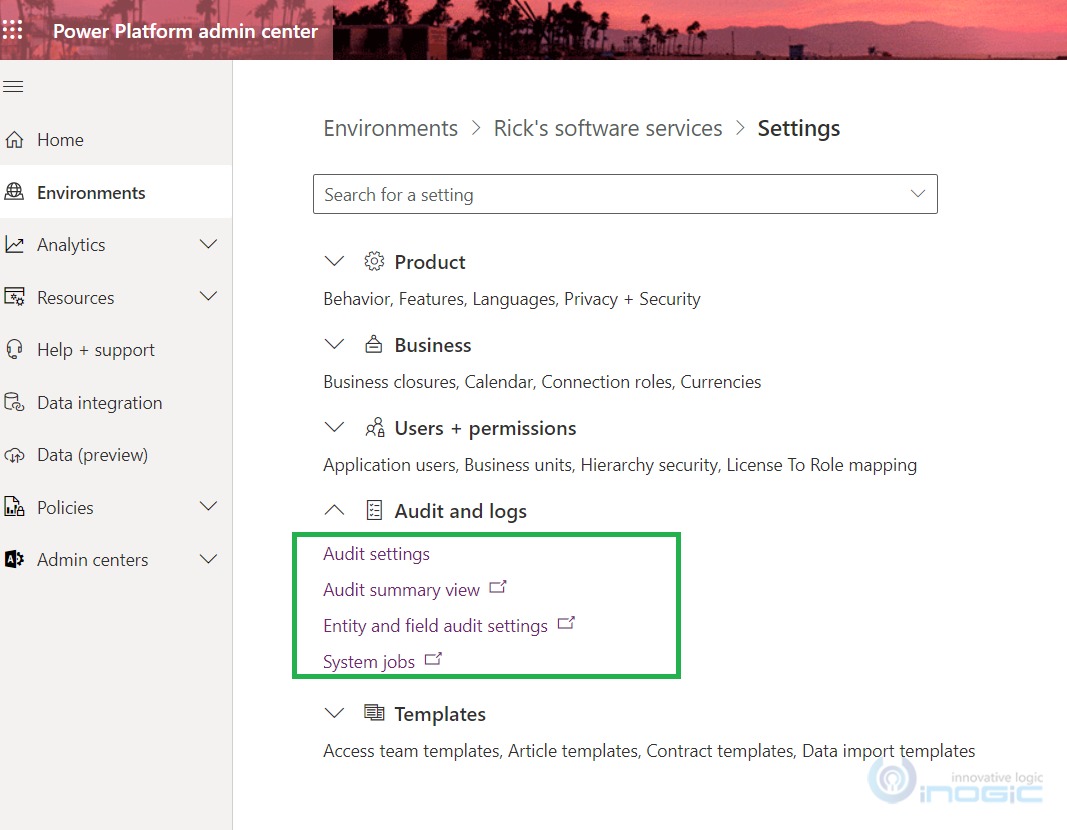
To explore this latest development, navigate to the auditing setting from the Power Platform admin center , then go to Environments > [select an environment] click on Settings > expand the Audit and logs as shown below:
You can find more details about the retention policy in this doc.
What’s New?
With the new audit management section, you can now easily manage logs more effectively by taking advantage of below-mentioned points:
- Audit retention settings
- Data management deletion options
Audit retention settings:
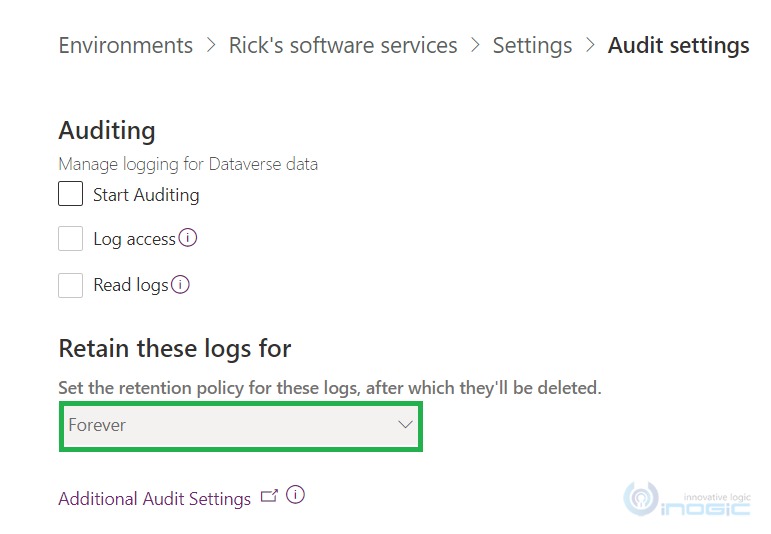
You can set a retention period for how long audit logs are to be kept in a Microsoft Dataverse environment. Under the “Retain these logs for” option, choose the period of time for which you wish to retain the logs.
Go to Power Platform admin center, navigate to Environments > [select an environment] click on Settings > expand the Audit and logs > Audit settings.
By default, the option selected in the “Retain these logs for” is ‘Forever’ and it is non- editable.
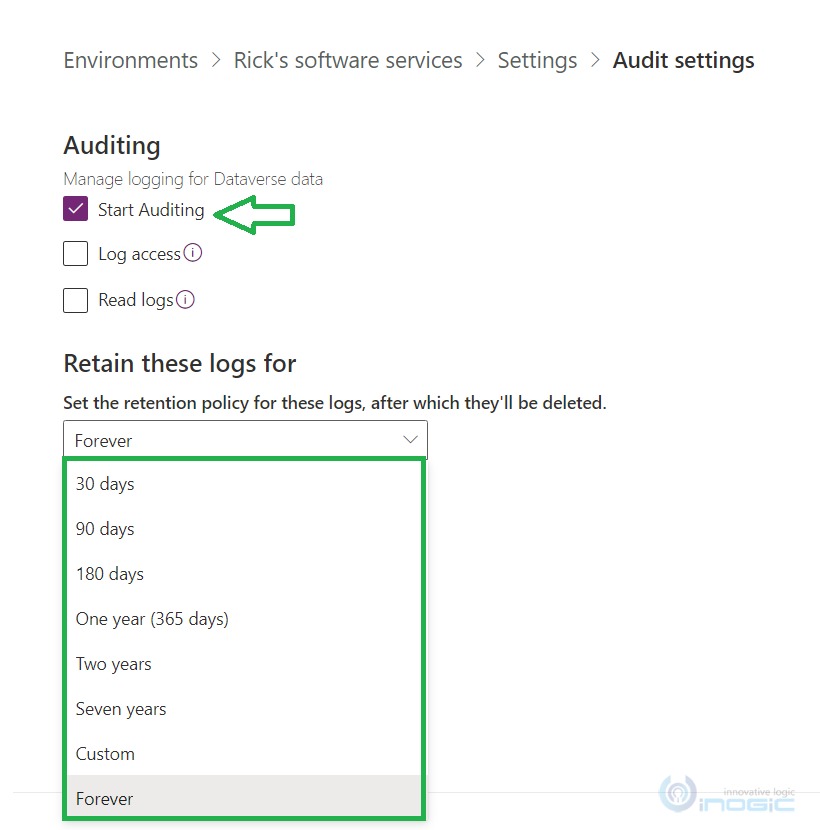
When you click on the “Start Auditing” check box it gets editable, and you can select any value from the list. The available options in the list are:
- 30 days
- 90 days
- 180 days
- One year (365 days)
- Two years
- Seven years
- Custom
- Forever
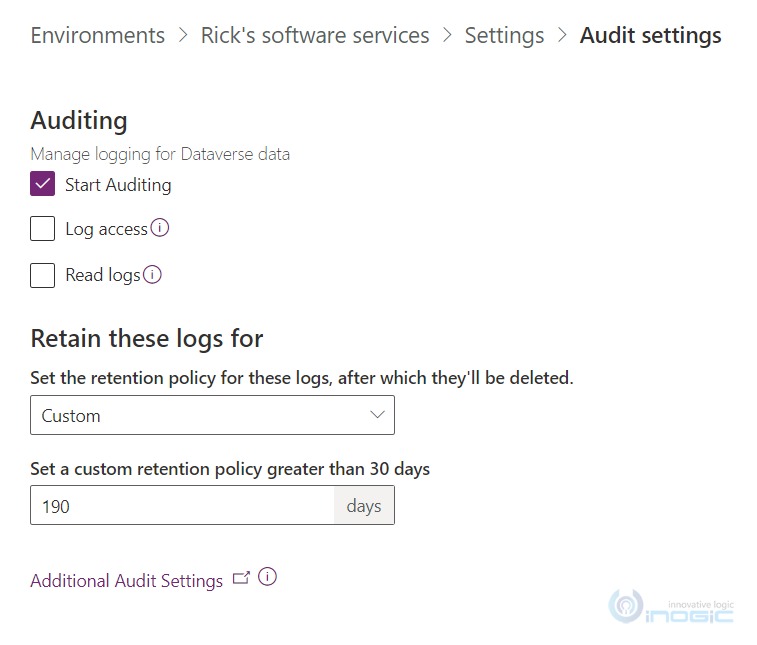
If you want to define your own option then you can go for the “Custom” option as shown below:
NOTE: The lower limit for defining custom value is 30 days and the upper limit is 365,000 days. Changing the retention period will not change already existing audit logs and is only applied to newly created audit logs.
Data management deletion options:
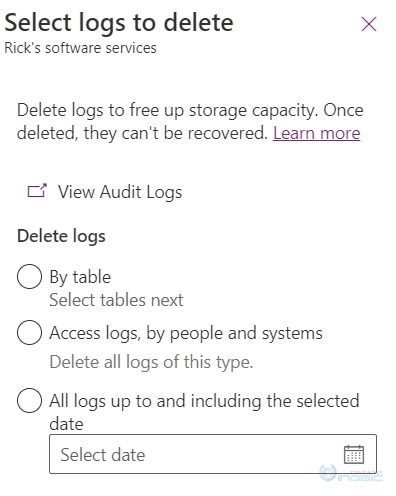
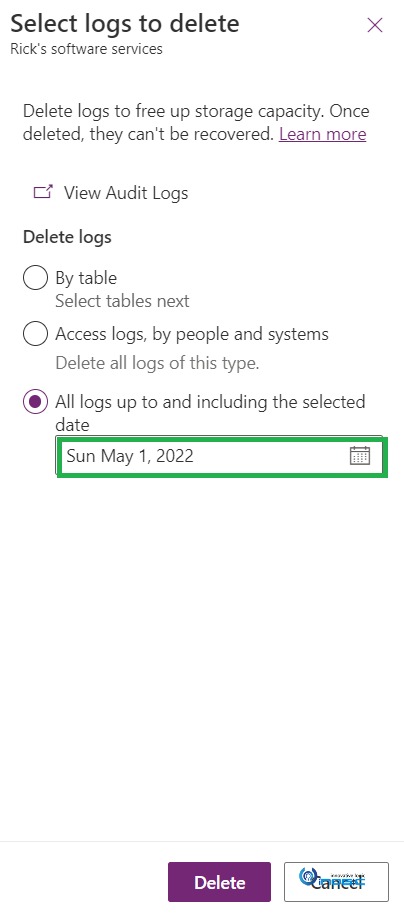
Go to Power Platform admin center> Environments > [Open an appropriate environment] under Auditing > Go to “Free up capacity” > click on > Delete logs.
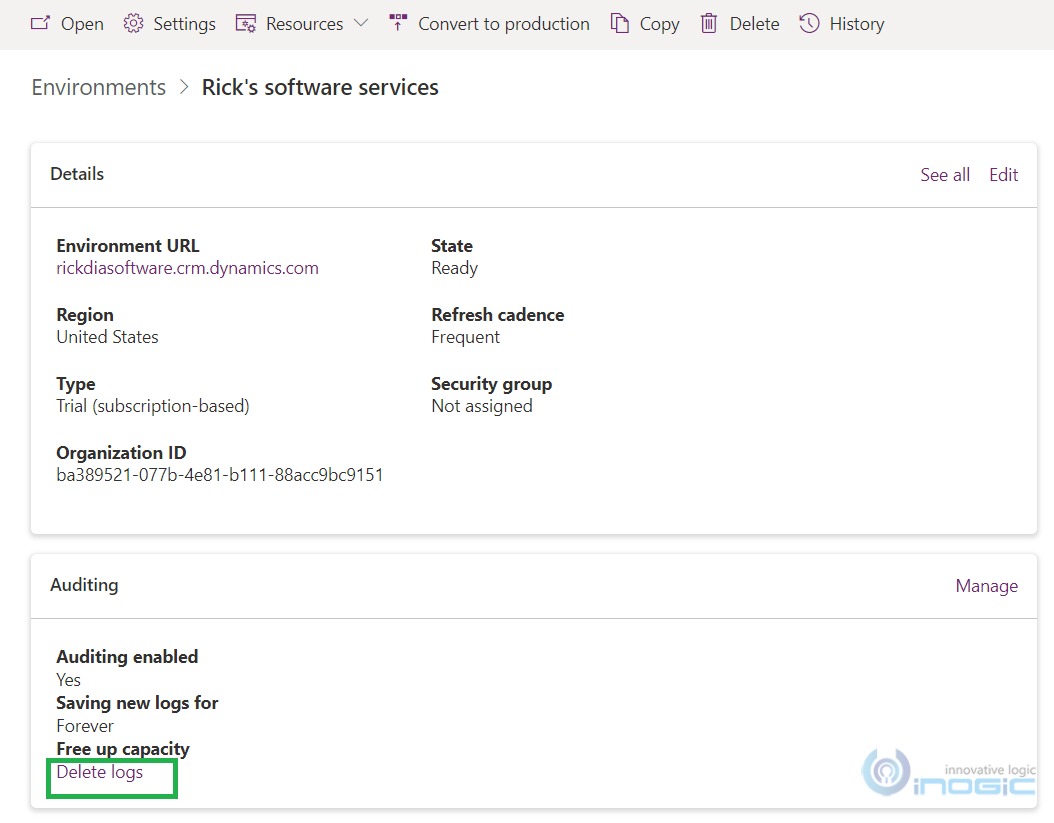
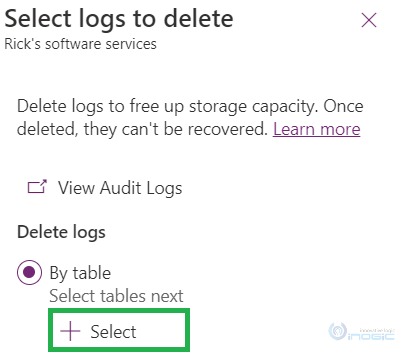
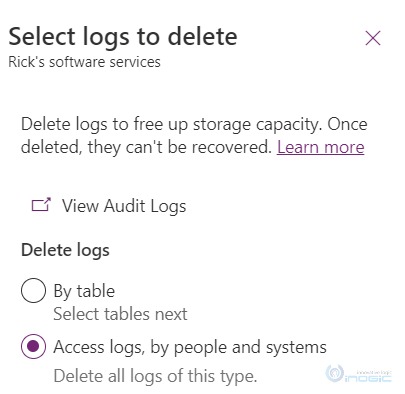
After clicking on “Delete logs” you will see the 3 available options – By Table, Access logs, by people and systems, and All logs up to and including the selected date.
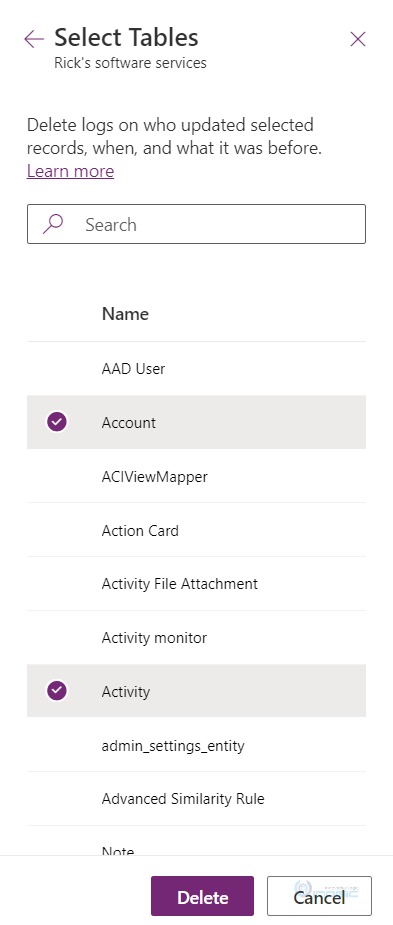
By table: Selecting this gives you the option to select the table you would want to delete all logs for.
You can select one or multiple tables from below table lists:
Access Logs, by people and systems: Selecting this will allow you to delete all access logs i.e. who was accessing the system.
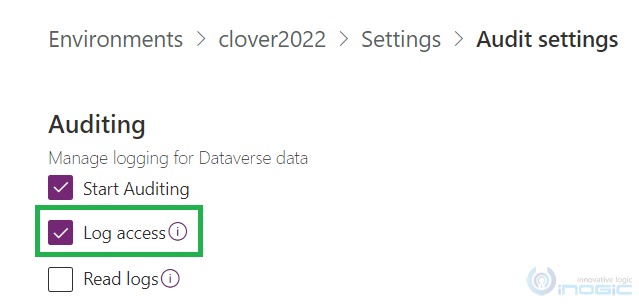
NOTE: Before using “Access logs, by people and systems” option to delete the logs make sure in your organization you have audit log present with operation as Access. If not then make sure you have selected the “Log access” check box and after that, you will observe the access audit logs are being created.
Go to Power Platform admin center> Environments > [Open an appropriate environment] under Settings > Audit settings > Log access.
All logs up to and including the selected date: Selecting this gives you the option to delete logs for a given date range.
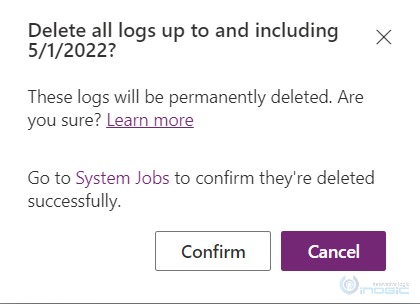
NOTE: When you click on “Delete” button, the confirmation pop-up will be displayed as shown below:
You need to click on the confirm button.
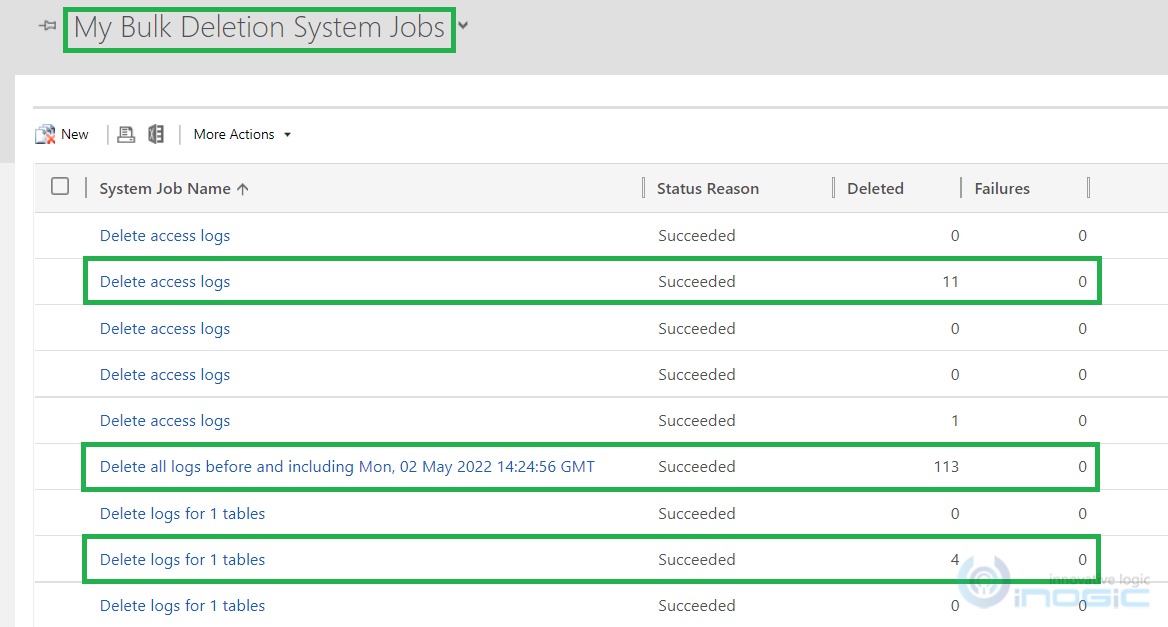
Go to Power Platform admin center> Environments > [Open an appropriate environment] under Settings > Go to Data Management > click on Bulk deletion.
You can verify the bulk deletion system jobs created and it starts deleting the logs for every corresponding option selected above as shown below:
You can find more details about reducing the amount of storage space in the organization from this doc.
NOTE:
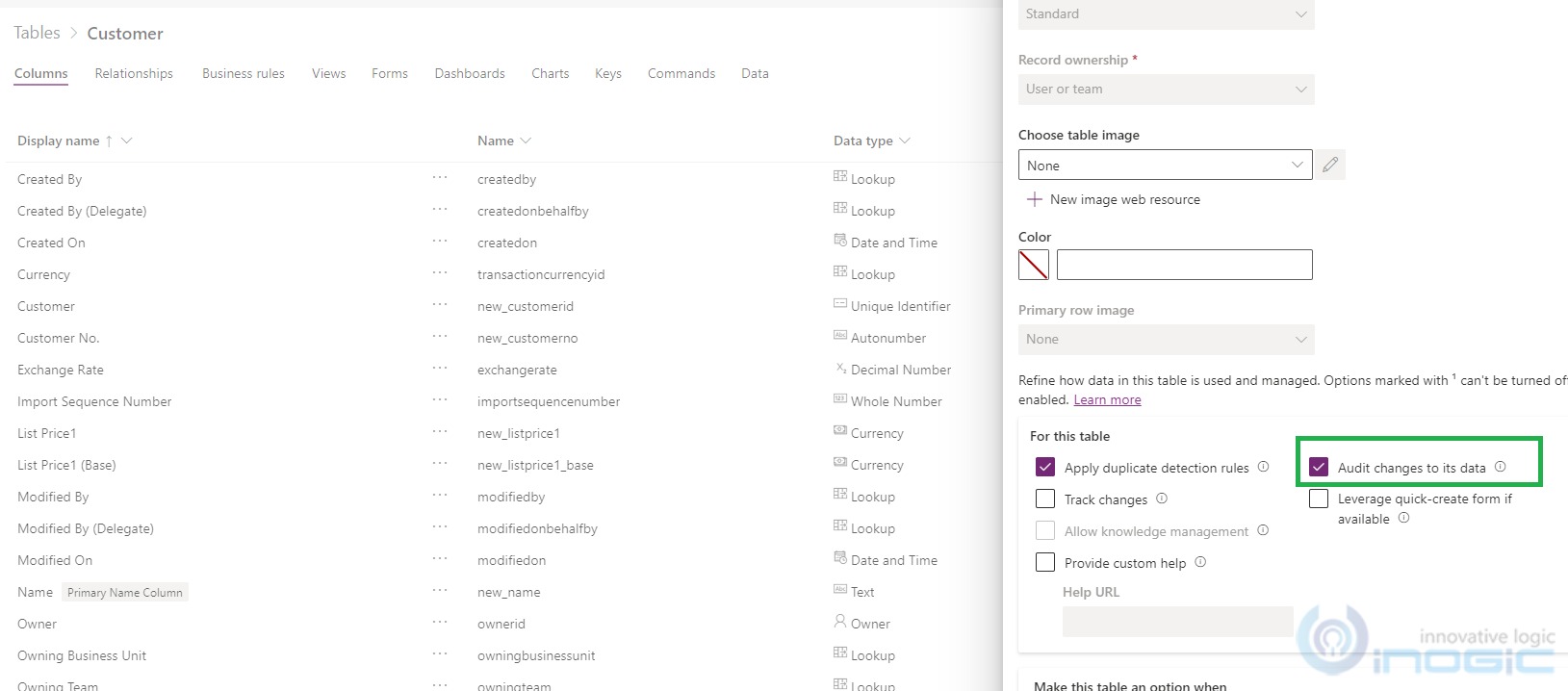
While turning on the Auditing for any entity, moving forward be aware of the current organizational audit retention policy.
The no. of days set in retention period do have impact on retaining the audit logs for entities and once those days are met, audit logs won’t exist further in the organization as they are auto-deleted.
Currently if user tries to turn on auditing for the entity, there is no way by which the users can be aware of the current retention policy in days defined in the background.
So before turning on auditing, users must go to Environments > [select environment] click on Settings > expand the Audit and logs > Audit settings and be aware of the current retention policy. This way they can know till when those logs would be retained in the organization.
Conclusion
With the new audit retention settings and data management deletion options, users will now be able to manage logs more effectively and can reduce the storage space. This will help them to significantly increase the size of the organization’s database.